Table of Contents
ToggleTreatments & Expertise
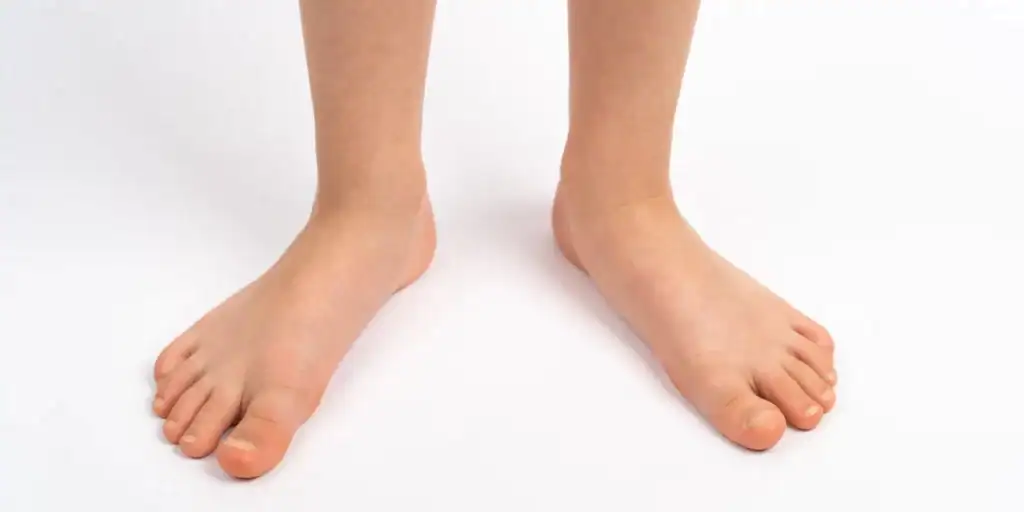

Does Your Child Suffer from Flatfoot (Pes Planovalgus)?
Visit Dr. Qureshi, a leading paediatric orthopaedic surgeon in Dubai, for expert paediatric flatfoot treatment. Pes planovalgus, commonly known as flatfoot in childhood, can affect foot alignment and comfort. Dr. Assad carefully selects nonoperative strategies as the first line of treatment before considering surgical options. Book an appointment now to give your child the best possible paediatric orthopaedic care. At every stage, we put your child’s health and well-being first.
Assess and treat your child’s flatfoot early
Flat feet are very common in the general population and usually cause no problems. They are seen in most infants and young children where it is very unusual to have any complaints other than their appearance. The arch usually develops during childhood so many parents just require re-assurance. According to Dr. Qureshi, Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon UAE, there is no scientific evidence to support insole use to encourage the arch to develop faster or to a greater degree in healthy young infants.
Flat feet may become symptomatic in the teenage years as calf muscles tighten during growth spurts and the child gains weight. In most cases, a good insole or orthotic helps support the arch and straighten the heel, making walking long distances more comfortable. Physiotherapy can also help stretch calf muscles and make the foot more flexible and pain-free, providing reliable options for flatfoot pain treatment in Dubai.
Surgery for symptomatic flat feet is best reserved for cases where nonoperative measures such as physiotherapy and orthotics have failed after extended follow-up. For families seeking advanced flatfoot treatment in Dubai, surgical intervention could be discussed once conservative options are exhausted.
There are many different surgical options available for flatfeet treatment in Dubai. Joint fusion surgery to eliminate movement in certain joints and keep the foot straight is usually reserved for severe cases with neurological causes. Subtalar implants involve inserting an implant into the hindfoot to push bones apart and straighten the heel. These non-biological reconstructions remain debated regarding patient suitability and long-term outcomes.
Dr. Qureshi prefers a personalized biological flat foot reconstruction technique, employing osteotomies and soft tissue rebalancing. Tailored to the patient’s unique deformity, the operation typically involves a thoughtfully chosen combination of the following surgical techniques:
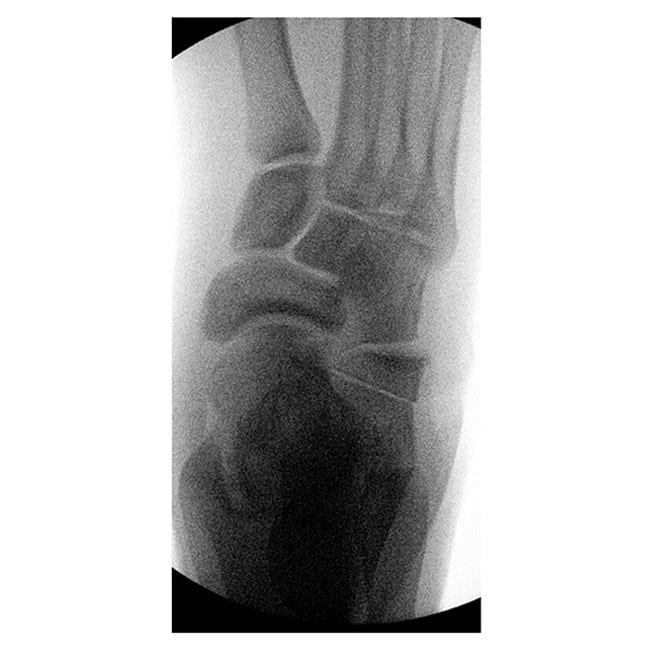
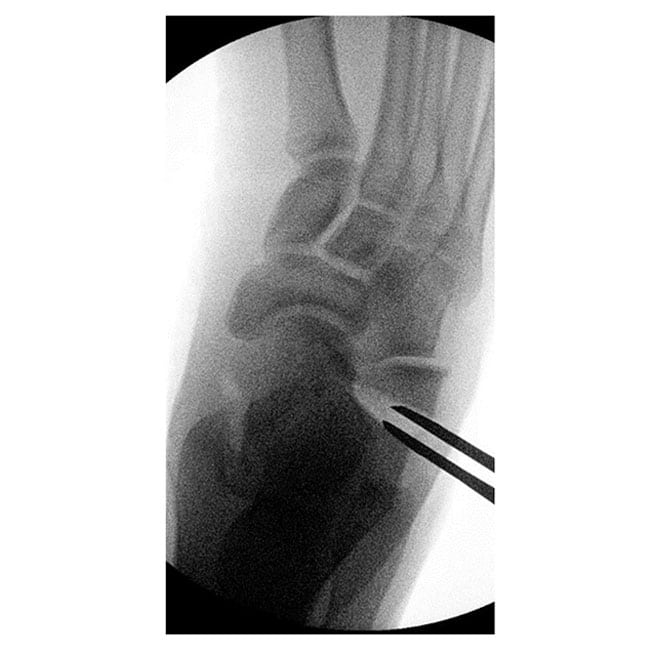
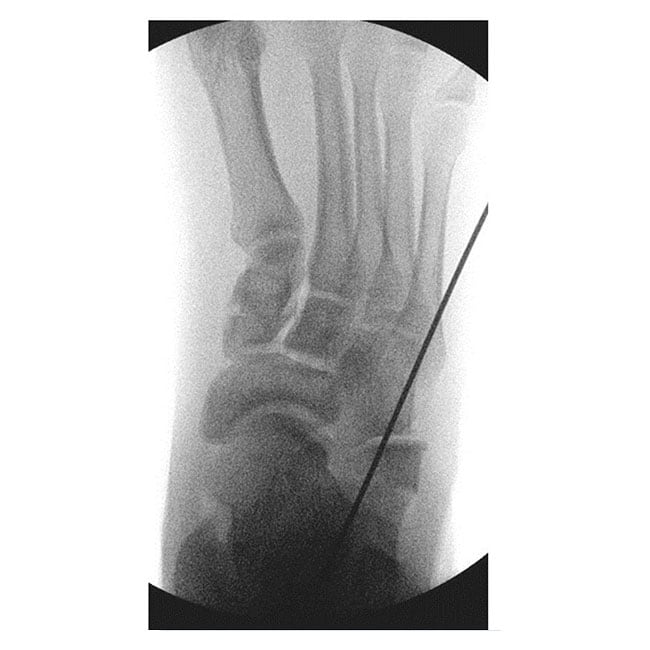
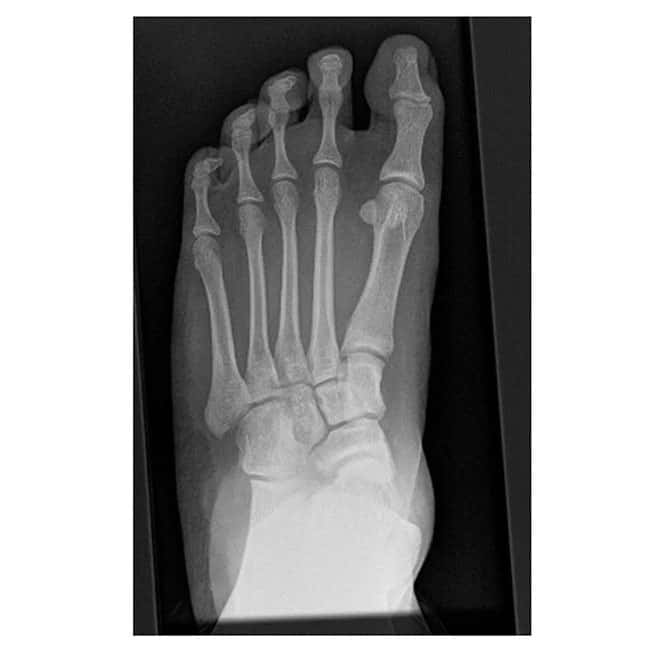
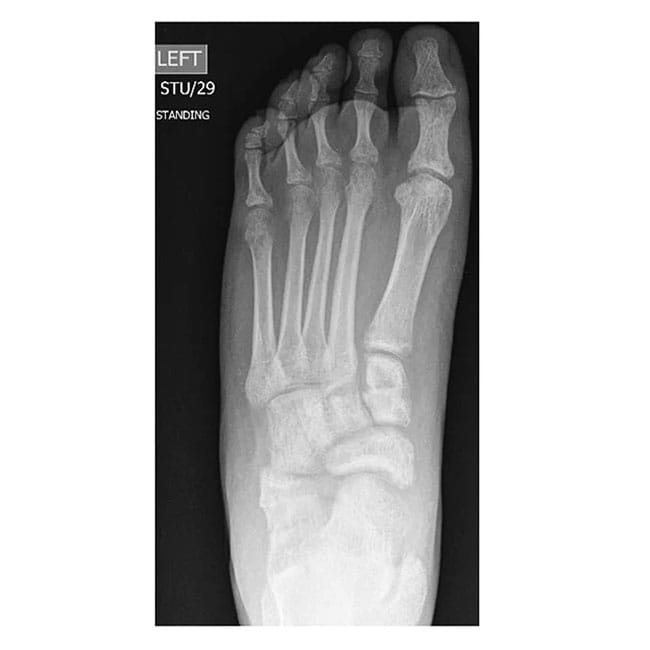
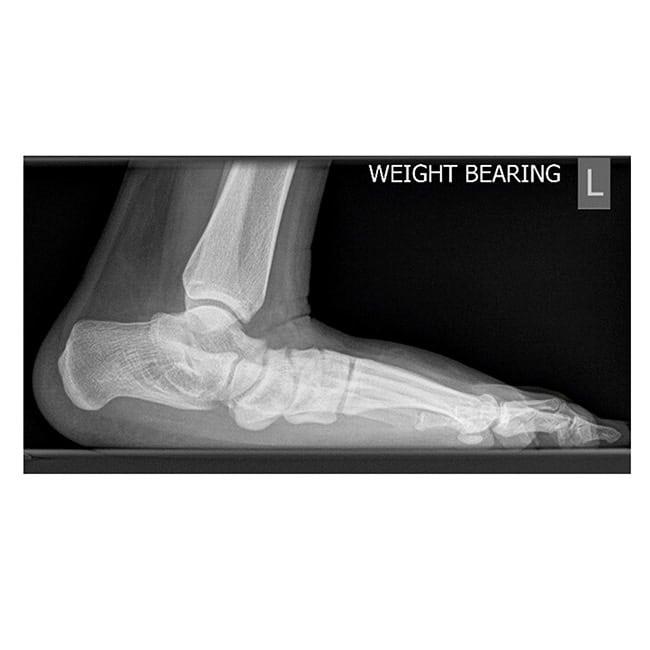
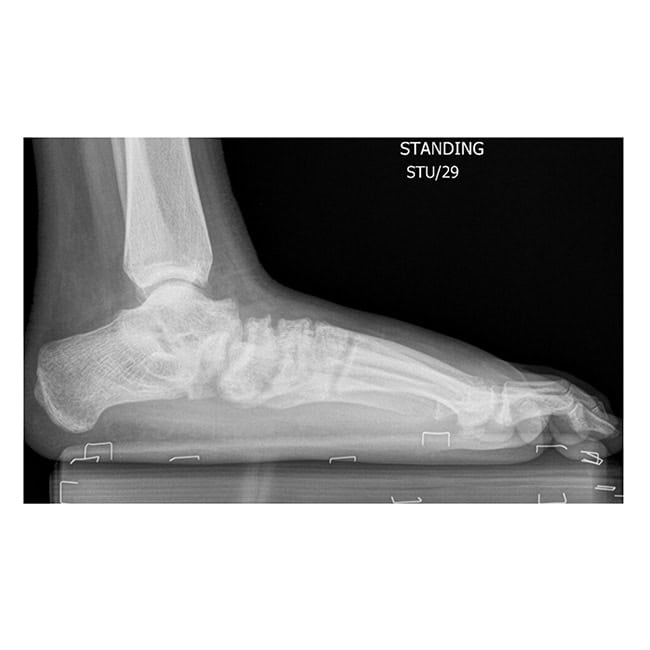
- Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy: This is a procedure that deals with the lengthening of the heel bone and straightening of the outer border of the foot. The bone division is carefully opened, achieving the desired correction, and supported with a bone graft typically sourced from the pelvis. The patient’s own bone is usually the best choice, although commercially available bone grafts can be used.
For consultations or further details, please contact us.
Case A: 15 year old with right flat foot showing calcaneal lengthening osteotomy
- Heel shift osteotomy: In severe cases where the heel points outwards, a calcaneal lengthening osteotomy alone may be insufficient so a separate osteotomy to realign the heel beneath the leg may be required.
- Medial cuneiform osteotomy: This osteotomy is used to augment the arch on the inner border of the foot
- Tibialis posterior advancement: The tibialis posterior tendon is responsible for pulling up the arch of the foot so this procedure tackles any slack by re-tensioning the tendon.
- Calf muscle complex lengthening: If there is significant tightness, lengthening of the involved muscles or the combined Achilles tendon may be included in the surgical plan.